Jamabandi is a critical document in the revenue field of Pakistan, particularly in the management of land records. It serves as the Record of Rights (RoR) for a village or a specific revenue estate and is maintained by the Revenue Department. Here’s a detailed overview:
Key Features of Jamabandi:
- Ownership Record: It contains detailed information about the landholdings in a revenue estate, specifying the names of landowners, the extent of their land, and the type of ownership (e.g., individual or joint).
- Cultivation Status: It records who is cultivating the land—whether it is the owner, a tenant, or another individual.
- Revenue Details: It specifies the land revenue or taxes payable to the government by the landowners.
- Mutation Updates: Any changes in ownership or rights (due to sale, inheritance, or other means) are reflected in the Jamabandi after the mutation process is completed.
- Cycle of Revision: In Pakistan, Jamabandi is typically updated every four years during the revenue settlement process.
Structure of Jamabandi:
A typical Jamabandi document contains:
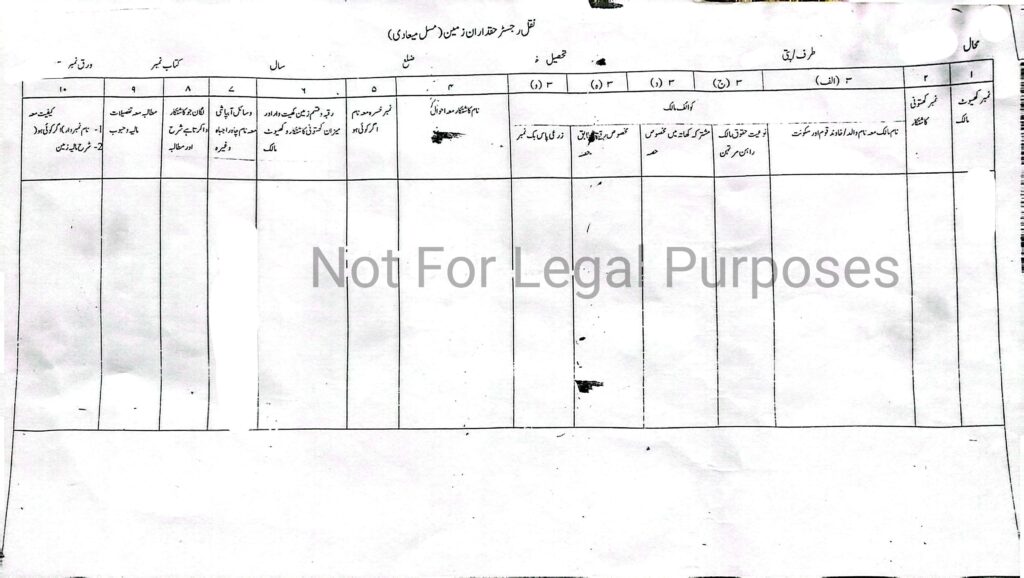
- Khewat Number: Identifies the ownership group.
- Khatauni Number: Denotes the holding of a particular cultivator.
- Khasra Number: Represents the specific plot or piece of land.
- Land Use: Specifies how the land is being utilized (e.g., agricultural, residential, commercial).
Importance of Jamabandi:
- Legal Proof of Ownership: It is a key document for landowners to prove their ownership rights in legal and administrative matters.
- Revenue Assessment: It forms the basis for assessing and collecting land revenue.
- Dispute Resolution: Used in resolving disputes related to ownership, tenancy, or land boundaries.
Jamabandi is an essential part of the land revenue system in Pakistan and is closely linked with other records, such as the Mutation Register (Register Haqdaran-e-Zamin) and Field Maps (Shajra Kishtwar).
FAQs
What is Jamabandi, and why is it important in Pakistan’s land revenue system?
Jamabandi is the Record of Rights (RoR) document maintained by the Revenue Department in Pakistan. It provides detailed information about land ownership, cultivation, and revenue details within a specific revenue estate or village. It is crucial for legal ownership proof, revenue assessment, and resolving land-related disputes.
How often is the Jamabandi updated, and what changes are reflected in it?
Jamabandi is typically updated every four years during the revenue settlement process. Updates include changes in ownership or rights due to sales, inheritance, or other transactions, which are recorded after completing the mutation process.
What are the key features of the Jamabandi document?
Jamabandi includes:
- Ownership Record: Names of landowners and details about their landholdings.
- Cultivation Status: Information on who is cultivating the land (owner, tenant, or others).
- Revenue Details: Taxes or land revenue payable to the government.
- Mutation Updates: Reflects changes in ownership or rights.
What components and numbers are recorded in a Jamabandi document?
Jamabandi contains the following key components:
- Khewat Number: Identifies the ownership group.
- Khatauni Number: Denotes the holding of a particular cultivator.
- Khasra Number: Represents the specific plot or piece of land.
- Land Use: Indicates the purpose of the land, such as agricultural, residential, or commercial use.


Leave a Reply